How To Recruit
& Becoming Recruited
Simon Mika
Simon Mika
Mentor
- development managers
- project managers
- product managers
- lead developers
- scrum masters
Advice
- agile development
- lean startup methodology
- system architecture
- developer recruitment
Build
- development organizations
- products and prototypes
Preparing
Be Ready to Move Fast
- plan process
- formulate requirements
- delegate decision and negotiation
Outpace your Competition
Employees Market
- Adapt your plans to what's available.
Sourcing
Ads
- Platsbanken, Arbetsförmedlingen (it's free)
- Stack Overflow
- LinkedIn (easy apply)
Network
Good People know other Good People.
Routinely Interview New Employees for Candidates:
- University Classmates
- Former Colleagues
- Friends
Example: Google
Search
- Github
- Stack Overflow
Example: Google
Events
Host, Sponsor or Talk at Events.
Builds long term brand and awareness in the community.
Example: Caspeco
University
- Thesis Workers
- Trainee Programs
- Sponsor Events
- Ads
Long term brand building pays of even for small companies.
Example: Precisit
Selection
Selling
Convincethe candidate that your company is where they want to work.
Do
- Move fast, decide continuously
- Get buy in from existing staff
- Be decent, say no to candidates
Don't
- Focus on imperfections
- Look for perfection
- Interview without goal
- Waste candidates time
Initial Selection
- Weed out unqualified candidates
- Look for uneven candidates
Warning Example: Amazon
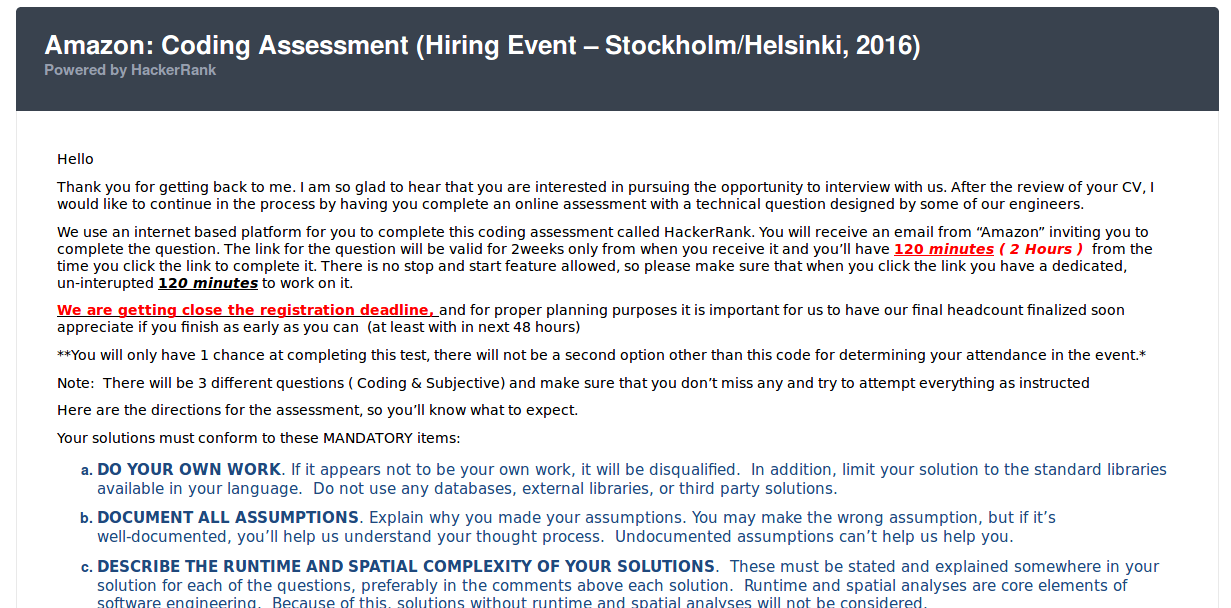
Warning Example: KnowIT
Invite to Interview
- Offer interviews at start and end of the day
- Who to meet, where, when and how long
- Be fast, invite continuously
First Interview
- Prepare room and printed resume
- Say hello, offer coffee or water, show office, sit down
- Explain recruitment process
- Talk about yourself, the company and the position
- Open up for questions
- Let them tell about themselves, follow in resume
- Ask questions (salary, period of notice)
- Open up for questions
- Next steps
Warning Example: Google
Only focus on programming skills, not selling the position.
Competence Interview
- simulate real work
- write code
- leave plenty of time
- leave candidate alone
- discuss choices
Warning Example: Google

Culture Interview
- eat lunch
- involve other employees
- avoid homogenization
- combine with competence interview
Closing
Make an offer that is:
- fair
- complete
- binding
- time limited (1-3 days)
Do
- Explain contract in detail
- Include phone number to ask question
- Include contract return envelope
- Require them to notify you of their decision by text/phone
Don't
- extend time
- reopen negotiation
- offer trial employment to employed candidates
Onboarding
Before
- start 1 hour after everybody else
- prepare table, chair, computer, phone, email, etc
- put flowers and business cards on desk
First Hour
- offer coffe and water
- introduce to 2-3 other employees
- show desk and help login
- setup accounts, clone repo
- show relevant example code
First Day
- start coding on first task
- lunch with new colleage on company expense
- show time reporting
- hand out keys
First Task
- finishable within 8h
- standalone
- datastructure for library
- focus on process not content
Second Task
- finishable within 2 weeks
- something new
- establish core competence
First Week
- one on one with manager
- bank account
- vaccation plan
- candidate recommendations
Becoming Recruited
Resume
- name, photo, contact details
- description
- competences
- employments
- education
- projects
Do
- use standardized personal letter and adapt it
- send out many applications at once
- know what you want and accept when you get it
Conclusions & Questions
Simon Mika